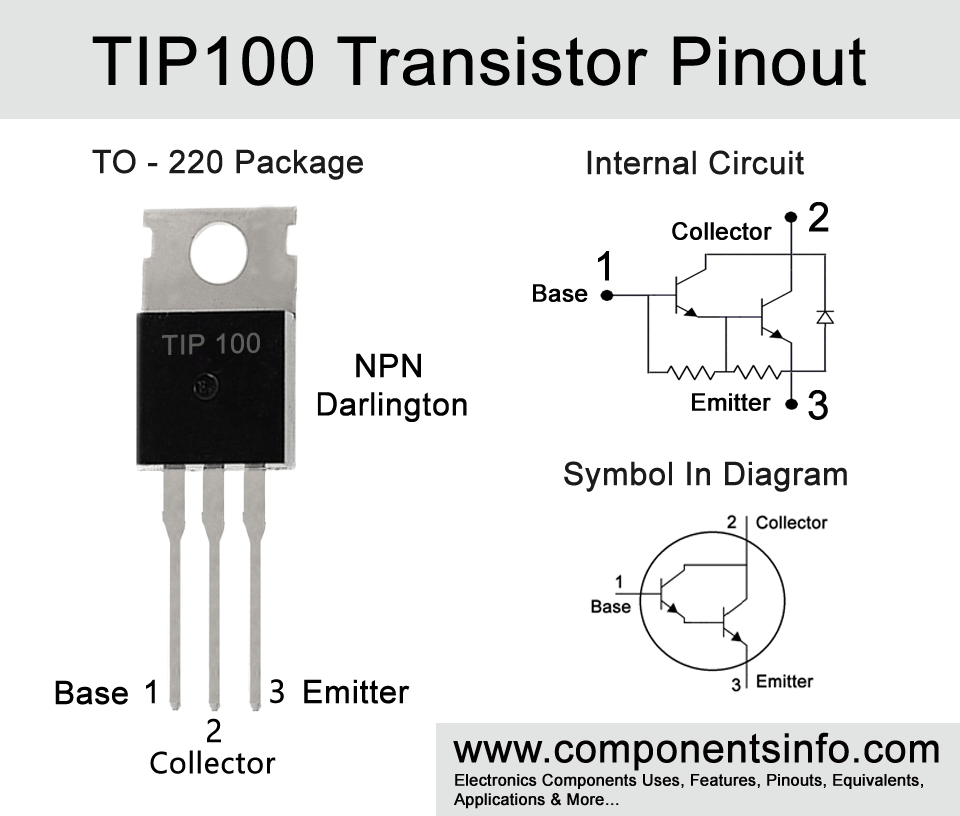
TIP100 Transistor Pinout, Applications, Equivalent, Features, and other Info
TIP100 is a medium power dalington trasnsistor from TIP series. It is a versatile transistor designed to use in various types of general purpose applications. It is an NPN transistor available in TO-220 package. Today we will understand TIP100 transistor pinout, applications, equivalent, features, where and how to use and other details about this transistor.
Features / Technical Specifications:
- Package Type: TO-220
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC): 8A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 60V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): 60V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Total Power Dissipation (PD): 80 Watt
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 1000 To 20000
- Max Storage and Operating Temperature: -65°C to +150°C
PNP Complementary:
NPN Complementary of TIP10O is TIP100
Replacement and Equivalent:
TIP101, TIP102, NTE2343, 2SD1525, 2SD1123, BD901, BD899, BC897, BD807, BD799, BD651, BC647, BD543, BD537, BD203, 2N6388, 2N6387.
TIP100 Transistor Explained / Description:
TIP100 is a medium power transistor available in TO-220 package. It is a darligton transistor means contains two transistors inside connected in a special way to increase the gain to a very high level. The internal diagram of the two transistors inside can be seen in the image above. The transistor is designed to use in general switching (low-speed type) and general amplifier applications.
TIP100 is a transistor of the TIP10x series, the other transistor of this series are TIP101, TIP102, and TIP102. The series of its complimentary transistors are TIP105, TIP106, and TIP107.
Now understanding the maximum ratings of the transistor, the maximum collector to emitter voltage is 60V which means this transistor can drive a load that requires a max voltage of 60V, its collector to base voltage is 60V it is the max voltage the transistor is capable to handle between its collector and base. its emitter to base voltage(VEBO) is 5V (VEBO) is the maximum voltage we can apply between emitter and base, the collector current of the transistor is 8A which means it can drive load of up to 8A, its total power dissipation is 80W, the total power dissipation is the value which shows the total energy or power that transistor consumed and dissipate the most of that power as heat, the dissipation of this heat is important so the transistor can work properly. However excessive heat generation of more than 80W is above the capability of this transistor and can cause damage to the transistor. its operating and storage junction temperate range is -65°C to +150°C means that this transistor will perform stably when it is used between this temperature range but outside of this temperature range the transistor will not perform stable, its lifespan will be reduced or it also get damage immediately.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
The transistor can be used in variety of switching, amplification, audio, and other circuits such as power control, voltage regulation, sensor circuits, instrument circuits, etc.
For using the transistor first of all check the pin configuration and then connect the “Base” with the input signal, “Emitter” with the ground or negative, and “Collector” with the output or load you want to drive.
Applications:
Low speed switching
Driving or switching loads upto 8A
Tone Control Circuits
Relay Drivers
Inverter Circuits
Instrument Circuits
Sensor Signal Conditioning
Audio amplifier circuits
Battery charger circuits
Motor driver circuits
Portable and battery-operated applications
Industrial Applications
Educational Applications
Lighting and Display Control
Home Automation
Robotics
Security Devices
How to Safely Long Run in a Circuit:
To properly use the transistor it is important to understand the safe operating guidelines.
- Make sure you do not exceed the maximum voltage ratings.
- Do not exceed the limit of collector current and peak collector current.
- Always check the total power dissipation and make sure that it is under the max limits.
- Use protection techniques such as diodes to prevent the transistor from voltage spikes.
- Make sure to operate or store the transistor between its max temperature limits.
- Always use a proper and suitable heatsink
- It is better to use it at least 20% below from its max ratings.
.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://z3d9b7u8.stackpathcdn.com/pdf-down/T/I/P/TIP100_FairchildSemiconductor.pdf