BD436 Transistor Pinout, Features, Equivalents, Applications and Other Details
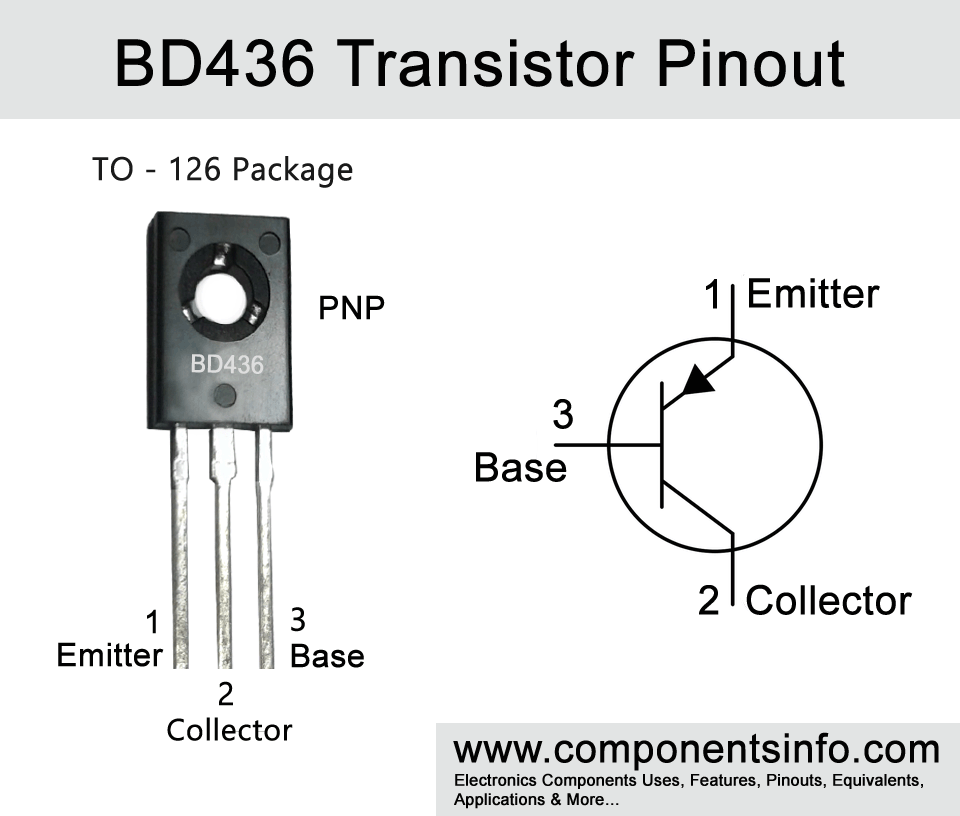
BD436 is a PNP transistor available in TO-126 package. This article contains information about BD436 transistor pinout, features, equivalents, applications and other details about this device.
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
- Package Type: TO-126
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Max Collector Current(IC): -4A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): -32V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): -32V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): -5V
- Max Collector Power Dissipation (PC): 36W
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 3 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 – 140
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: -65 to +150 Centigrade
NPN Complementary:
The NPN complimentary of BD436 is BD435
Replacement and Equivalent:
BD438, BD440, BD442, MJE223, MJE220, BD787, BD439, BD437, BD187, 2N4922, BD338, BD284, 2SB995, 2SB992, 2SB966, 2SB577, 2SB1372, 2SB1347, 2SB1163, 2SB1161, 2SB1158, 2SB1156, 2SB1154.
BD436 Transistor Explained / Description:
BD436 is a medium power PNP transistor available in TO-126 package. It is a transistor of BD43x series which also contains other transistors such as BD434 and BD438. These transistors can be used as equivalents but the main difference between these transistors are their VCBO, VCEO and VCES voltages. The BD434 has lower voltages than BD436 so you can only replace it if your circuit is working under -22V. But the other one BD438 can be replaced without any hassle because its VCBO, VCEO, and VCES voltages are higher than BD436.
The absolute maximum ratings of the transistor are collector-base voltage (VCBO) is -32V, collector-emitter voltage (VCEO) is also -32V, collector current is -4A, emitter-base voltage is -5V, base current is -1A, and collector dissipation is 36W.
Now looking at some electrical characteristics of the transistor the transition frequency of the transistor is 3MHz, max collector-emitter saturation voltage is -0.5V and minimum and maximum DC current gain is 40 to 140.
Where We Can Use it & How to Use:
The transistor is mainly designed for linear and switching applications but can also be used in automotive circuits, drivers, controllers, etc. More of its applications can be found under the applications heading below.
Moreover, regarding to using the transistor, the using procedure of the transistor is the same as we use any other BJT transistor.
Applications:
Inverter Circuits
Relay drivers circuits
Battery Chargers
Switching Circuits
PWM controllers
Motor Drivers
LED Drivers
Audio Amplifiers
Temperature Control Circuits
Battery Chargers
Solar Circuits
Variety of General Purpose Applications
Safe Operating Guidelines:
Here are the safe operating guidelines of the transistor.
- For safe operating, it is important to not drive the transistor to its absolute maximum ratings and always stay 20% below from its max ratings.
- So according to this 20% rule the maximum collector current is -4A, but we will only use 3.2A by driving the maximum load of not more than 3.2A.
- The maximum collector to emitter voltage is -32V, so we will not drive load of more than 25V.
- And the storage and operating temperature of the transistor should be between -65°C to 150°C.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://datasheetspdf.com/pdf-down/B/D/4/BD436_FairchildSemiconductor.pdf