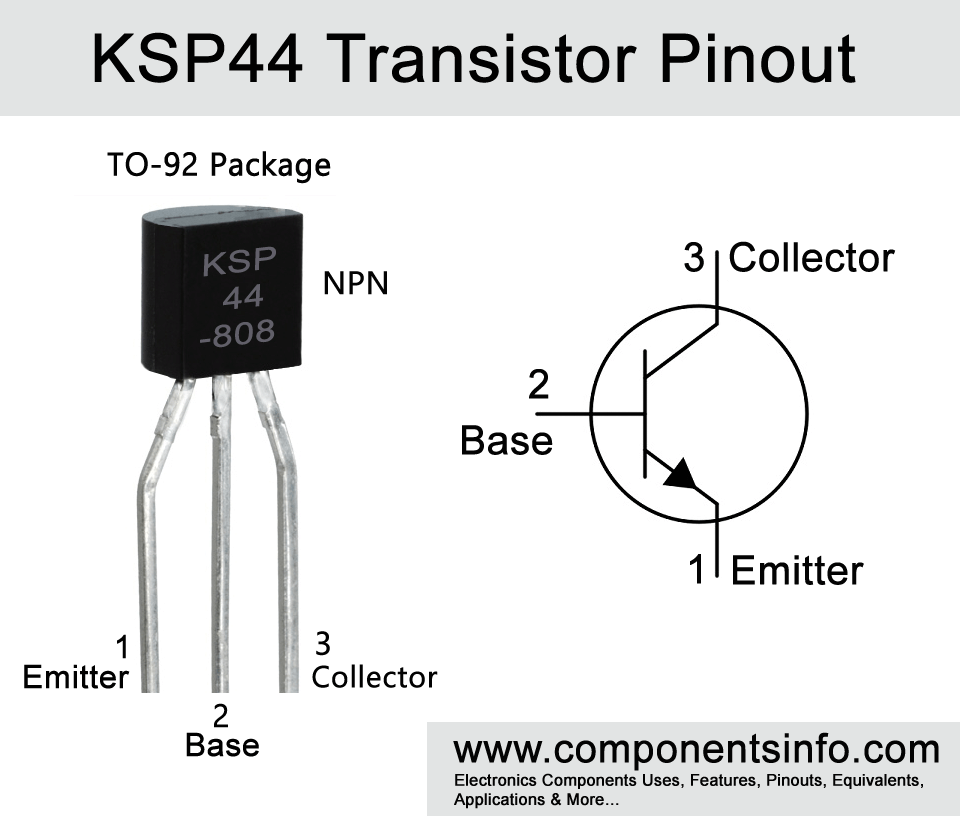
KSP44 Transistor Pinout, Equivalent, Features, Applications, How to Use and More
KSP44 is an NPN silicon high voltage transistor available in TO-92 package and is capable of driving a load of up to 400V. In this article, we are going to look deep into the KSP44 transistor explaining its pinout, equivalent, features, applications, how to use, and more.
Features / Technical Specifications
- Package Type: TO-92
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC): 300mA
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 400V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): 500V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 6V
- Max Collector Dissipation (Pc): 625 milliwatt
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 to 200
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: -55 to +150 Centigrade
PNP Complementary:
PNP Complementary of KSP is KSP94.
Replacement and Equivalent
MPSA44, KSP44BU, KSP44TF
KSA1381 Transistor Explained / Description
If you are looking for a high voltage TO-92 package transistor then KSP can be an ideal candidate. The transistor can drive load of upto 400V and the maximum current drive capability is upto 300mA. Understanding other absolute maximum ratings of the transistor, it has the maximum collector to base voltage of 500V means it can handle maximum 500V between its collector and base without damage. The max emitter to base voltage of the transistor is 6V, this value shows the maximum limit of voltage the transistor can handle between the emitter and base. The maximum collector dissipation is 625miliwatt, this value shows how much power this transistor is capable of handling without getting damaged by heat.
Now looking at its electrical characteristics the minimum to maximum DC current gain of the transistor is 40 to 200. The DC current gain shows the capability of the transistor to amplify current. The collector to base breakdown voltage is 500V, as mentioned earlier this is the maximum voltage limit the transistor can handle between its collectors and base without getting damaged. Collector to emitter breakdown voltage is 400V which means this transistor can handle or is capable of passing 400V from its collector to emitter. Collector to emitter saturation voltage is 0.75 at IC=50mA, IB=5mA this means when you want to drive a load of 50mA you have to provide 5mA at its base and the voltage drop or saturation voltage between collector and emitter will be 0.75V approx.
Regarding the uses of the transistor, this transistor can be used in high voltage circuits as well as in normal voltage circuits under 12V and 24V.
Where & How to Use
This transistor is especially designed for high voltage applications but it can also be used in regular applications under 12V and 24V for switching and amplification purposes. The using procedure of this transistor is same as we use other normal voltage general purpose transistors such as 2N3904 etc.
Applications
High Voltage Switching
Low Voltage Switching
Audio Amplification
Signal Amplification
Sensor Circuits
High Voltage Relay Driving
Switching Loads under 0.3A
Safe Operating Guidelines
Safe usage guidelines are very important to understand for any electronic component and all components has some safe operating guidelines so the transistor too should be operated wisely to get long term and stable performance.
First of all it is important to not using the transistor to its absolute maximum ratings and always stay 20% below from its absolute max ratings. So we have to calculate the extract the 20% from all of its maximum value and then make sure to not exceed from these values. Therefore according to this rule the maximum collector to emitter voltage of the transistor is 400V so do not drive load of more than 320V, the maximum collector current is 300mA so the driven load should be under 240V and the operating temperature of the transistor should be between -55 °C to +150°C.
Datasheet
To Download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://z3d9b7u8.stackpathcdn.com/pdf-down/K/S/P/KSP44_FairchildSemiconductor.pdf