D468 Transistor Pinout, Features, Equivalents, Specification, Applications & Other Details
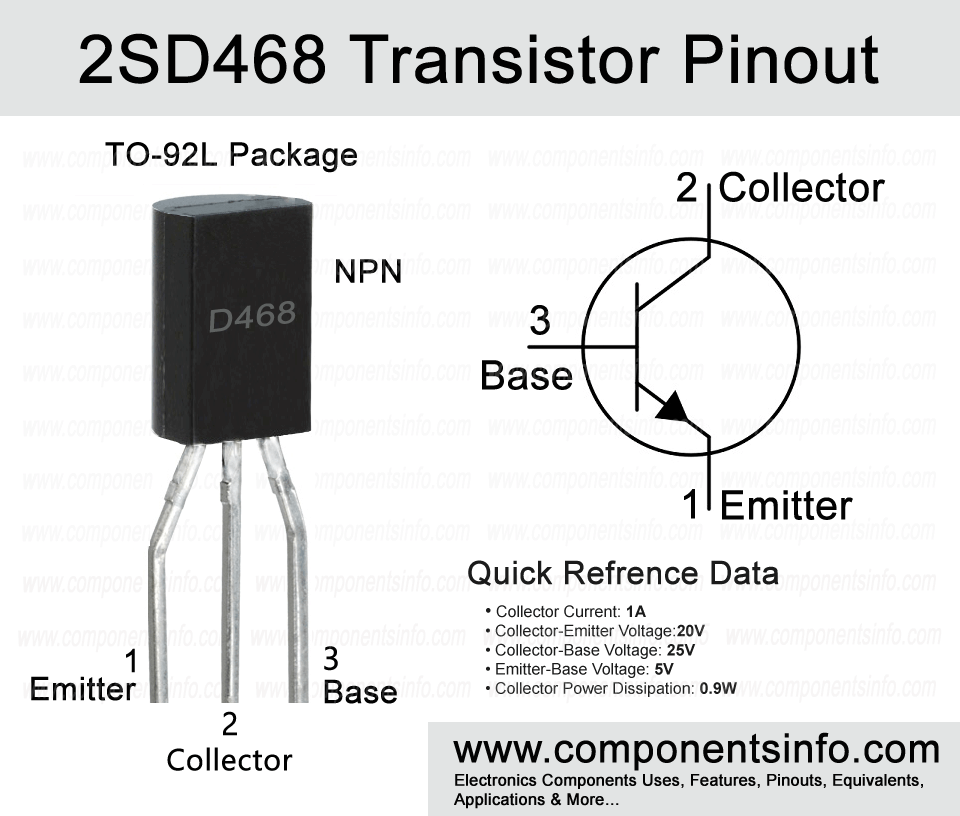
D468 full part number 2SD468 is an NPN transistor available in TO-92MOD package. It is designed for low frequency power amplifier applications but you can also use it in other applications which we will discuss later. This posts contains information about 2SD468 pinout, equivalents, features, uses, specifications and other details about this device.
Understanding the 2SD468 Transistor:
2SD468 is an NPN transistor. An NPN transistor contains three semiconductor layers namely N-type/P-type/N-type. The Emitter is an N-type region and it is heavily doped which means it contains many electrons that are ready at any moment. The base pin is a P-type region which controls how much electrons flow from the Emitter N-type to Collector N-type. The Collector pin has moderately doped region which means it collects electrons.
The transistor has some good features which are good collector current, transition frequency of up to 190MHz, DC current gain of 85 to 240 and availability of its PNP complimentary.
The collector-to-emitter voltage is 20V and can be used to drive a load below 20V. The collector current is 1A, so it can easily drive a load below 1A. However, these are absolute ratings, and the transistor should always be used at least 20% below its absolute maximum ratings. For example, if the collector-to-emitter voltage is 20V, then your load should not exceed 16V.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the transistor are as follows:
Pin1 is the Base pin: base pin control’s the flow of current from Emitter to Collector.
Pin2 is the Collector pin: The load is connected between the positive rail of the circuit and the collector pin. The current first enters in the load then goes to the transistor and then to the ground (Emitter pin) if the required base current is available at base pin.
Pin3 is the Emitter pin: The Emitter pin is the pin from which current flows to the outside of the transistor and reaches to the ground or negative rail of the circuit.
Here are the features and specifications of the transistor:
- Package Type: TO-92MOD
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Max Collector Current(IC): 1A
- Peak Collector Current(ICM): 1.5A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 20V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): 25V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Max Collector Power Dissipation (Pc): 0.9 Watt
- Minimum DC Current Gain (hFE): 85 to 240
- Max Storage & Operating temperature: -55 to +150 Centigrade
PNP Complementary:
PNP Complementary of 2SD468 is 2SB562
Replacement & Equivalent
2SD592A, 2SD545, BCX38, BC737, BC639, 8050, 2SD974, 2SD863, 2SD667, 2SD2181, 2SD1347, 2SD1247, 2SD1207, 2SD1146, 2SD1100, 2SD1045, 2SD1014, 2SC4682, 2SC4604, 2SC4169, 2SC3246, 2SC3225, 2SC2316.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Using 2SD468:
Here we are pointing advantages and disadvantages of choosing 2SC5763 for your circuit or applications.
Advantages:
Up to 1A Collector Current: With collector current of 1A you can drive many small loads.
Good Transition Frequency: The transition frequency of 190MHz makes this transistor suitable to use in RF applications of this frequency.
DC Current Gain: The DC current gain ranges from 85 to 240 which is also acceptable. The DC current gain shows the amplification capacity of the transistor.
Availability of Complimentary Transistor: The availability of its PNP complimentary transistor 2SB562 is also a good advantage because pairing both of these transistors allows more improved amplification and low crossover distortion.
Disadvantages:
Low Voltage: The collector-emitter voltage of the transistor is only 20V and the collector-base voltage is only 25V due to which you cannot use this transistor for high voltage applications.
Disadvantage of 1A Collector Current: Only 1A collector current can limit this transistor for applications that requires more than 1A current. There are many transistors of that package are available that has collector current of 2A or more.
Moderate Power Dissipation: The power dissipation value of only 0.9 Watts limits the transistor to be used in high power applications.
2SD468 Applications:
This transistor is specially designed for Low frequency power amplifie applications but due to its good specifications make it usable in variety of applications such as:
Audio Amplifiers
Signal Amplification
Switching Applications
Battery Operated Applications
Motor Driver for Small Motors
Conclusion:
The 2SD468 is designed to be used in Low frequency power amplifier but its good specs makes it a versatile transistor for other applications that falls under its ratings.
It has some good features / advantages such as 1A collector current good for small loads, good transition frequency, moderate DC current gain and availability of its PNP complimentary.
However, the transistor does have some limitations like its low voltage ratings, 0.9W power dissipation and only 1A collector current also limits this transistor and makes it suitable only for small and low current (Under 1A) applications.
Datasheet:
To download the datasheet just copy and paste the below link in your browser.
https://www.alldatasheet.com/datasheet-pdf/view/63042/HITACHI/2SD468.html