1N4001 VS 1N4007 – Discussing Differences, Similarities, and Interchangeability
In this post, we are going to discuss about 1N4001 VS 1N4007 diode. Both of these diodes are from the same 1N400X series which is available in DO-41 & SMD packages, it is a quite popular diode series and you will find the diode of this series in a variety of commercial equipment and appliances. Moreover, these diodes are also quite popular among electronic engineers, students, hobbyists & tinkerers. The diodes of the 1N400X series are called general purpose rectifier diodes, they are quite reliable and low cost diodes which are mostly used to convert AC voltage to DC in bridge rectifiers of power supplies, blocking voltage where required etc .
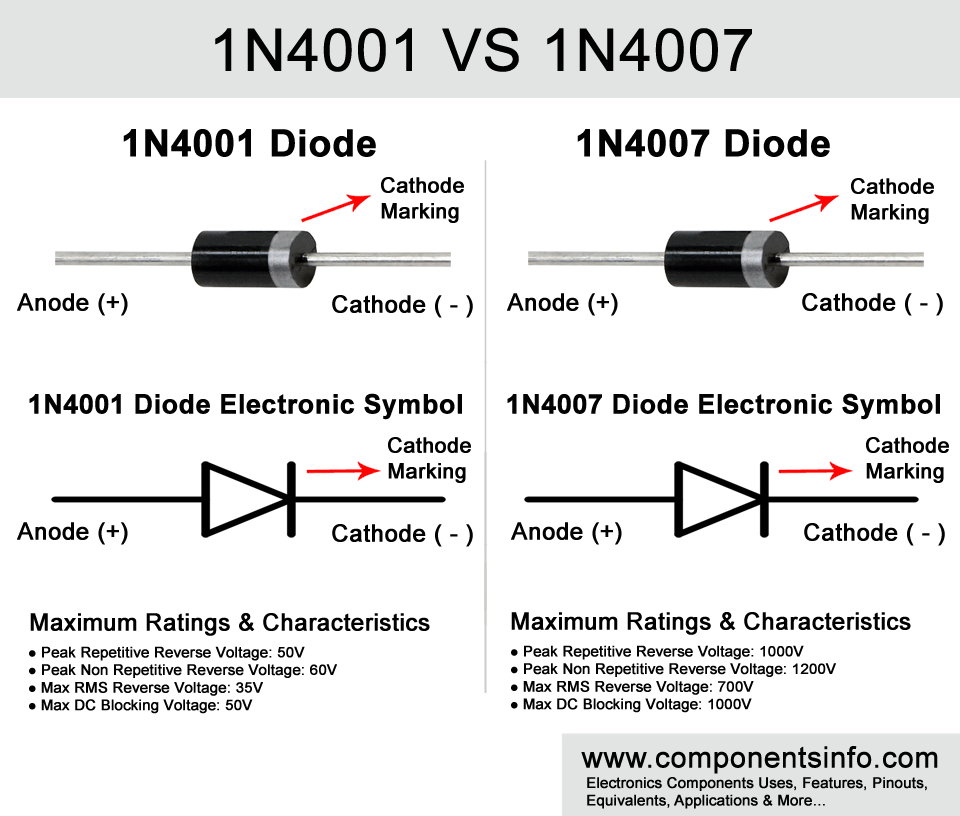
1N4001 VS 1N4007 Physical Appearance
As you can see in the 1N4001 vs 1N4007 image above both the diodes look exactly same in appearance because they are made in same DO-41 package and we cannot differentiate them without reading the part number written on them or testing its electronic characteristics with electronic testing equipment. But if a component looks similar from outside that doesn’t mean it is also similar from inside or similar in ratings and characteristics. Below we will dig deeper in both of the diodes and compare their ratings and characteristics and see the differences and similarities.
Ratings & Characteristics Comparison:
| Ratings & Characteristics | 1N4001 | 1N4007 |
|---|---|---|
| Max Repetitive Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | 50V | 1000V |
| Average Rectified Forward Current (Io) | 1A Or 1000mA | 1A Or 1000mA |
| Max Forward Voltage (VF) | 1.1V | 1.1V |
| Power Dissipation (PD) | 3 Watts | 3 Watts |
As you can see in the rating and characteristics of 1N4001 in the chart above its max repetitive reverse voltage is 50V, average rectified forward current is 1A, max fwd voltage is 1.1V, and power dissipation is 3 Watt. While the 1N4007 max repetitive reverse voltage is 1000V, average rectified forward current is 1A and power dissipation is 3 Watt. So there is a noticeable difference between these two diodes and cannot be used interchangeably in some conditions which we will discuss below.
Can We Use 1N4001 Instead of 1N4007
As we have discussed above the max repetitive reverse voltage of 1N4001 is 50V and 1N4007 is 1000V so you cannot use 1N4001 in place of 1N4007 in all conditions because 1N4007 has a higher repetitive reverse voltage. So if you want to use 1N4001 instead of 1N4007 then you have to check the load voltage connected to 1N4007 in the circuit or how much voltage is required by the circuit that is connected through the diode. If that voltage is above 40V (the max repetitive reverse voltage of 1N4001 is 50V but it is its absolute max rating and the manufacturers do not recommend using a diode on its absolute maximum ratings so as a rule of thumb we use it at least 20% below from its max ratings) then you cannot use 1N4001 in place of 1N4007 but if it is under 40V then you can use 1N4001 in the place of 1N4007.
Can We Use 1N4007 Instead of 1N4001
The 1N4007 diode has a higher max repetitive voltage than 1N4001 and also the other ratings are the same such as average rectified forward current, max fwd voltage, and power dissipation. So you can use 1N4007 diode instead of 1N4001 in any circuit or condition.
Conclusion
1N4001 and 1N4007 are the diodes of same series and they have some similarities and differences. 1N4001 has low max repetitive reverse voltage so you cannot use it in the place of 1N4007 in all conditions. You can only use it in conditions in which the load voltage is below 40V. But when it comes to using 1N4007 in place of 1N4001 you can use it in any condition because it has a higher max repetitive reverse voltage than 1N4001.
There are also other didoes in this series which are 1N4002, 1N4003, 1N4004, 1N4005, and 1N4006. They are manufactured in different versions that can be used according to the circuit’s requirements. The first diode of the series 1N4001 has low voltage ratings than the other higher number ones. The higher number has higher voltage and characteristics but average rectified forward current, max fwd voltage, and power dissipation values are the same in all diodes of this series, hence you can select the diode according to the load voltage requirement in your circuit or design.